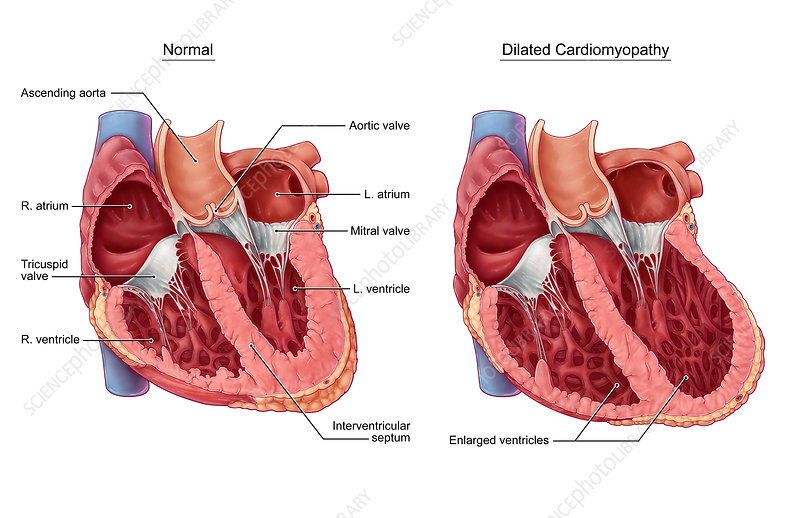
A comparative illustration of a normal heart and a heart affected by dilated cardiomyopathy. Dilated cardiomyopathy is the most common type of cardiomyopathy often caused by coronary heart disease, diabetes, alcohol abuse, viral infections, thyroid disease, or genetics. The walls of the ventricles stretch and thin (dilate), creating an enlarged heart. This inhibits the heart’s ability to pump enough blood throughout the body and may also result in abnormal heart beats (arrhythmia).
ABOUT US
About Us - At CPR and More, we are dedicated to empowering individuals and communities through comprehensive CPR training programs. With a nationwide reach and a commitment to local impact, we strive to equip people with the life-saving skills necessary to respond confidently and effectively in emergencies.
Our Services
Quick links
CPR News
[newsplugin_feed id='1635566777122' title='CPR' keywords='CPR | EMT' link_open_mode='_blank' link_follow='yes' count='5' wp_uid='10']Copyright © 2020 Education, All Right Reserved
Design by Grace Themes