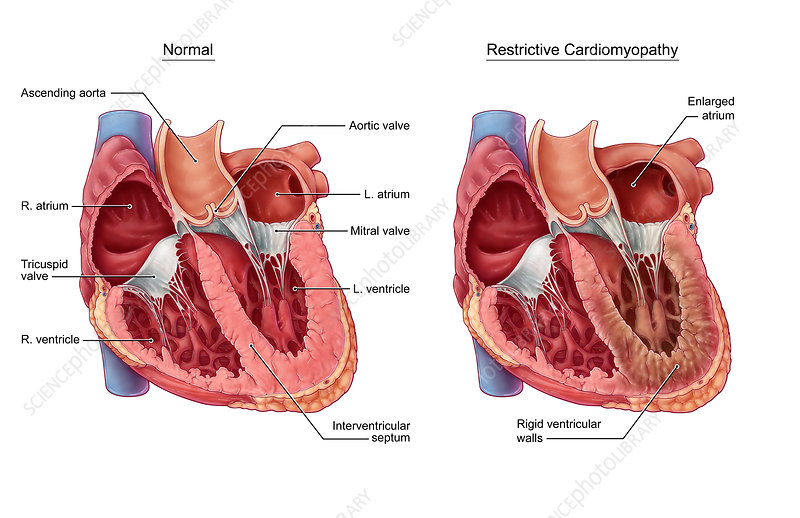
A comparative illustration of a normal heart and a heart affected by restrictive cardiomyopathy. Restrictive cardiomyopathy is a type of cardiomyopathy in which normal heart muscle is replaced by abnormal tissue, causing the ventricles of the heart become stiff and rigid. When the ventricles are unable to normally relax and fill with blood, the atria become enlarged and blood flow in the heart is reduced. Restrictive cardiomyopathy can be caused by diseases such as hemochromatosis, sarcoidosis, amyloidosis, or cancer treatments like radiation and chemotherapy.
ABOUT US
About Us - At CPR and More, we are dedicated to empowering individuals and communities through comprehensive CPR training programs. With a nationwide reach and a commitment to local impact, we strive to equip people with the life-saving skills necessary to respond confidently and effectively in emergencies.
Our Services
Quick links
CPR News
[newsplugin_feed id='1635566777122' title='CPR' keywords='CPR | EMT' link_open_mode='_blank' link_follow='yes' count='5' wp_uid='10']Copyright © 2020 Education, All Right Reserved
Design by Grace Themes